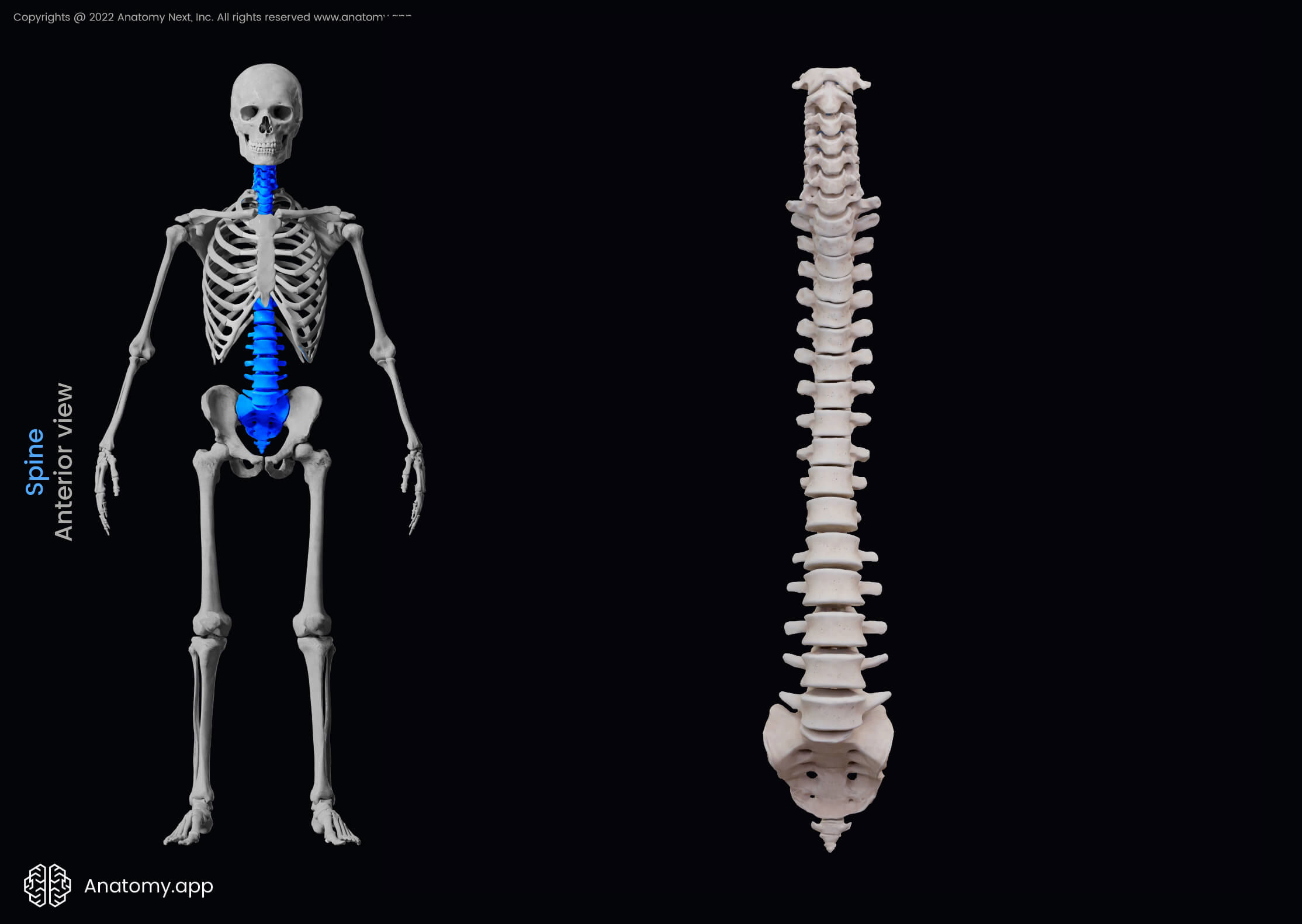
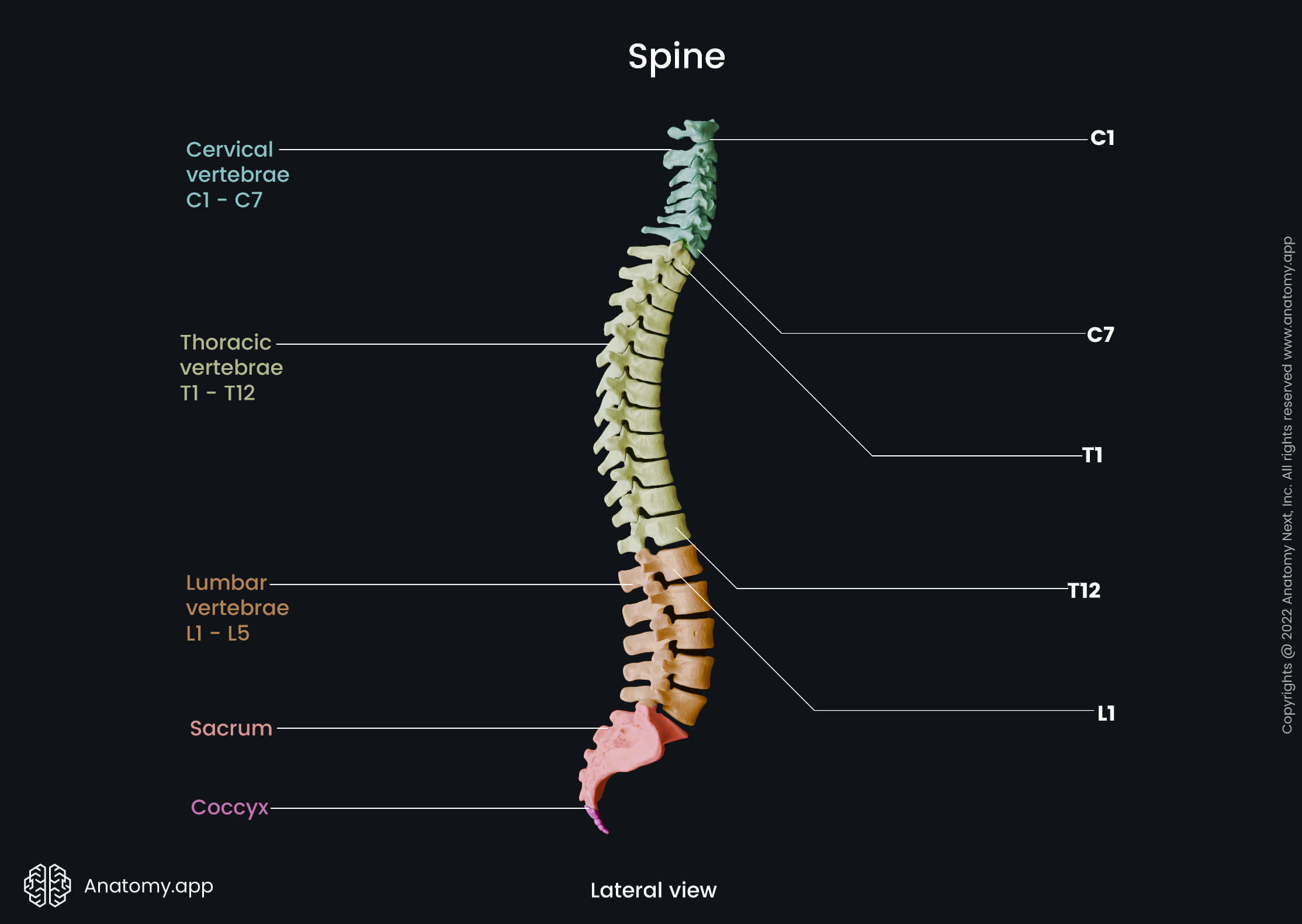
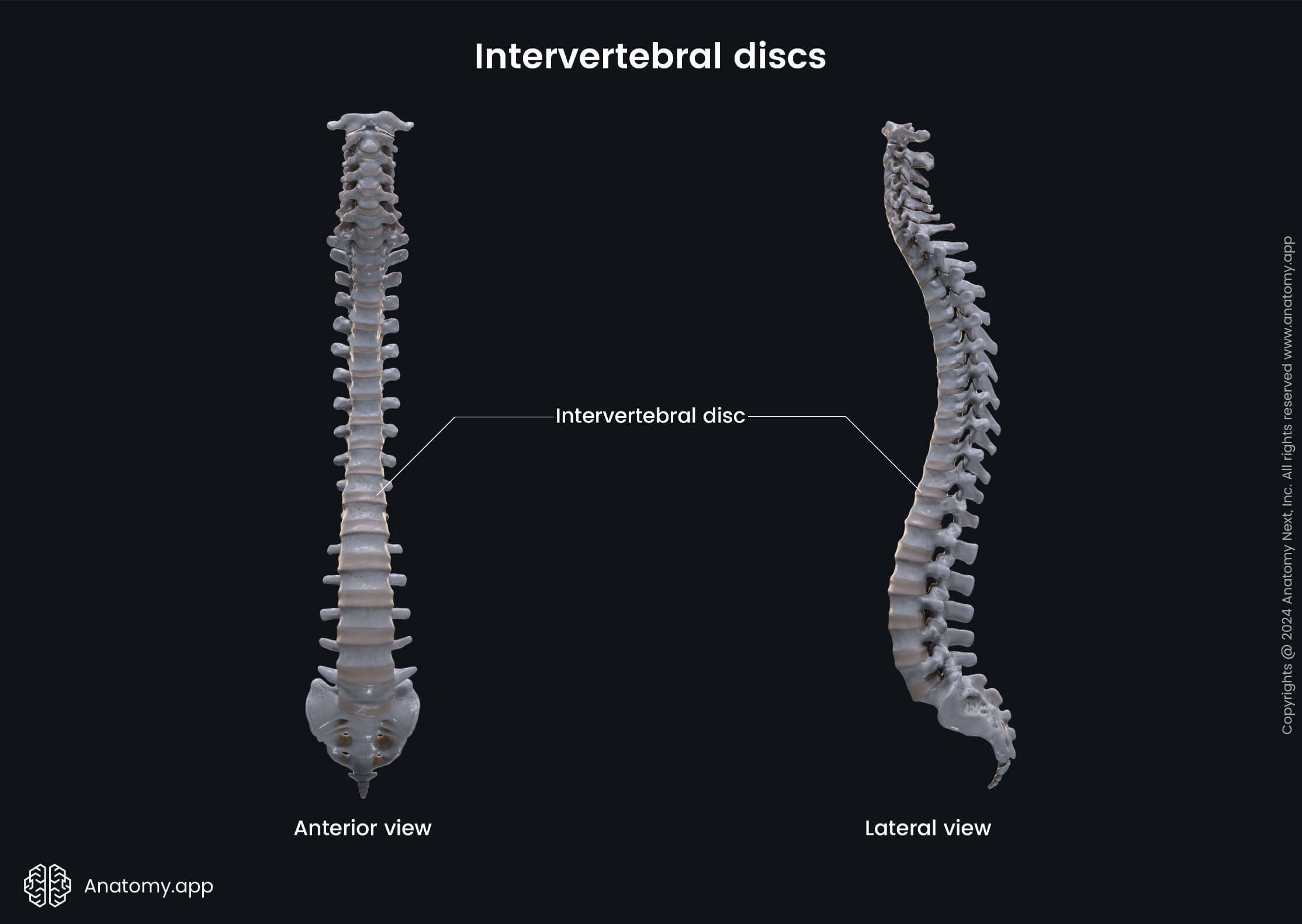
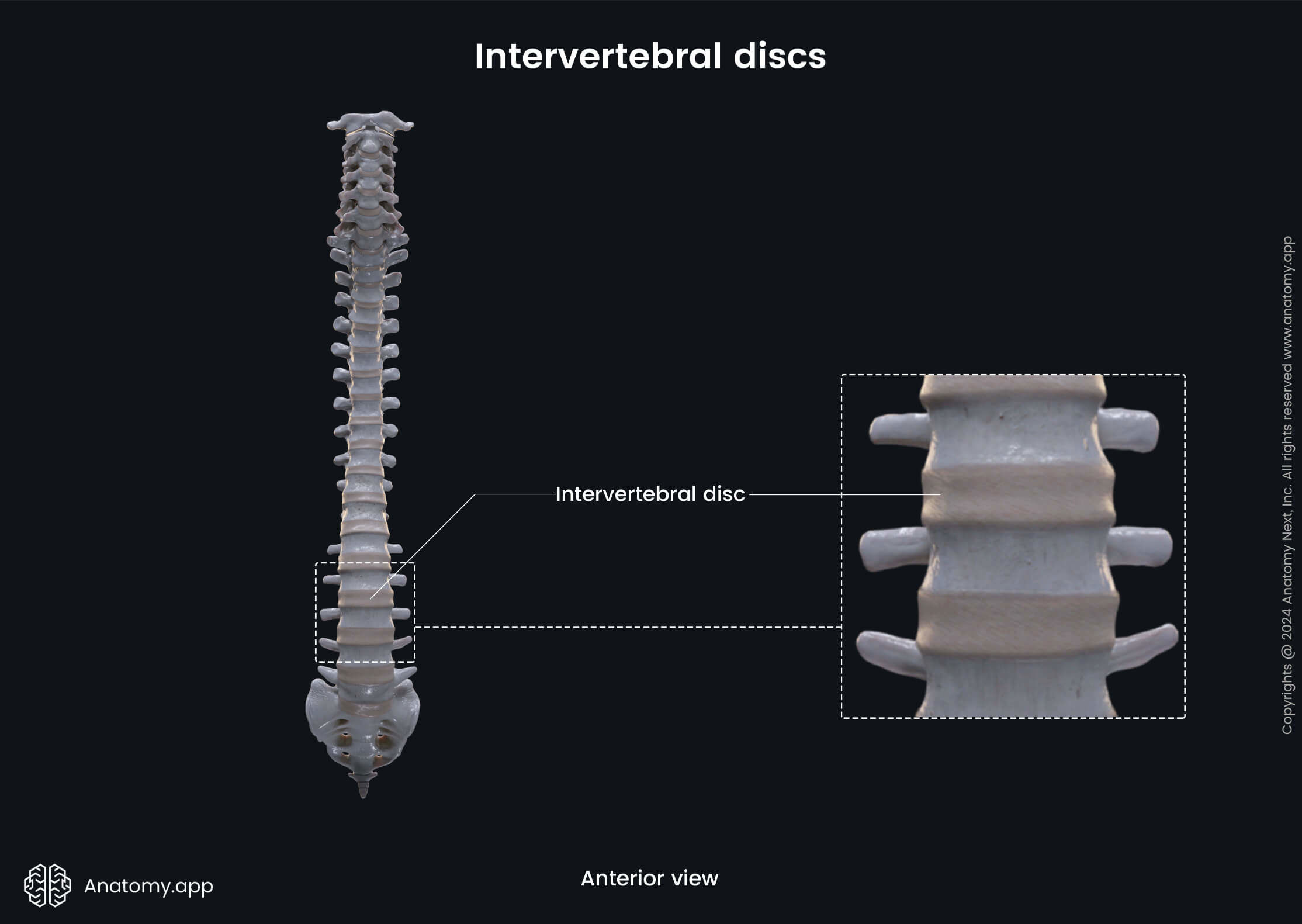
The spine or vertebral column (also known as backbone, spinal column, Latin: columna vertebralis) is a sequence of bones called vertebrae that are separated from each other by intervertebral discs. The spine forms the main axis of the human body.

The human spine is flexible and it supports the head, neck, and trunk allowing their movements. It also provides protection for the spinal cord, which is located within the spinal canal that is formed by central holes in the vertebrae.
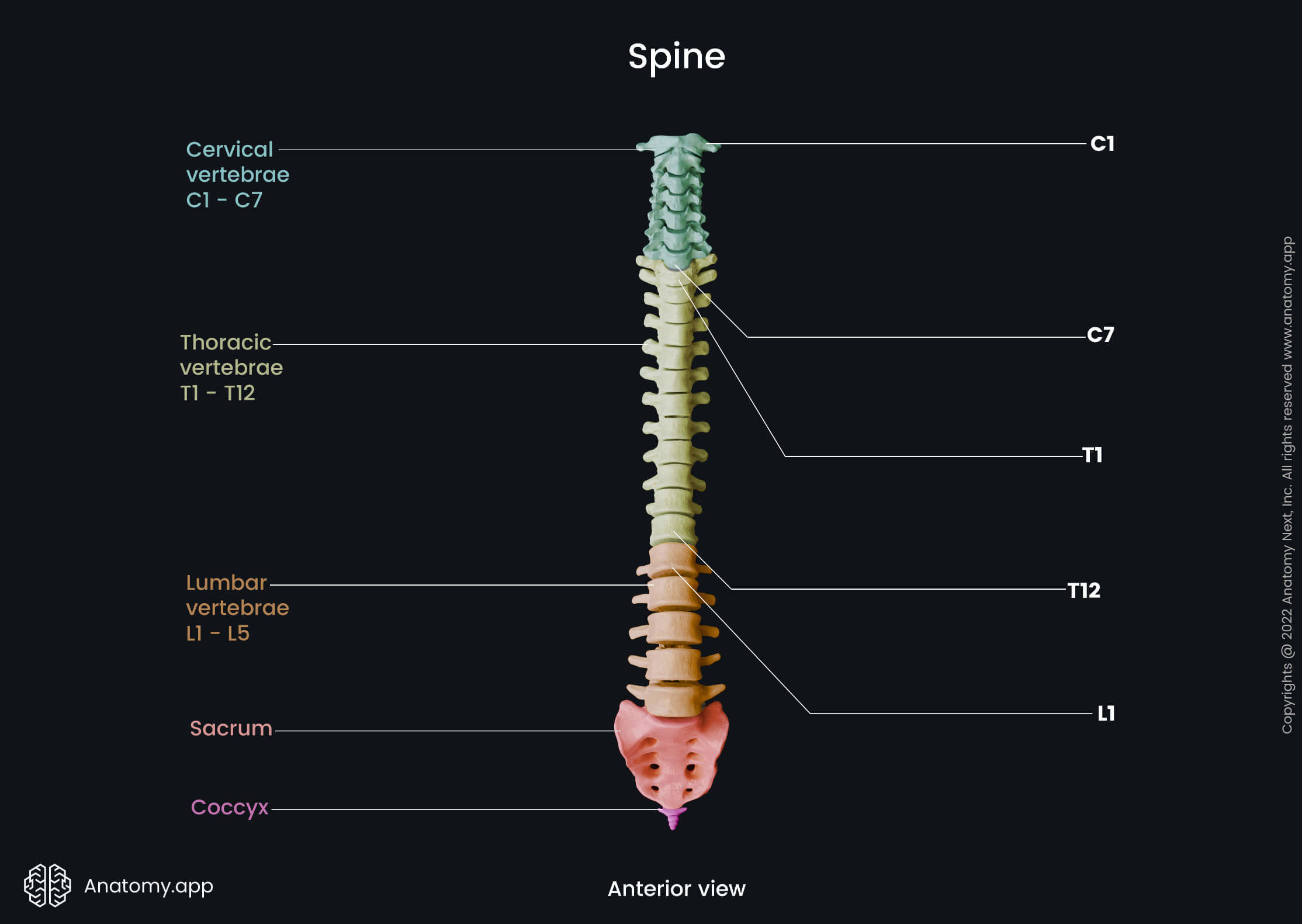
Normally, there are 32 to 34 vertebrae (singular: vertebra) forming the human spine. There are 24 free vertebrae and 8 to 10 fused vertebrae.
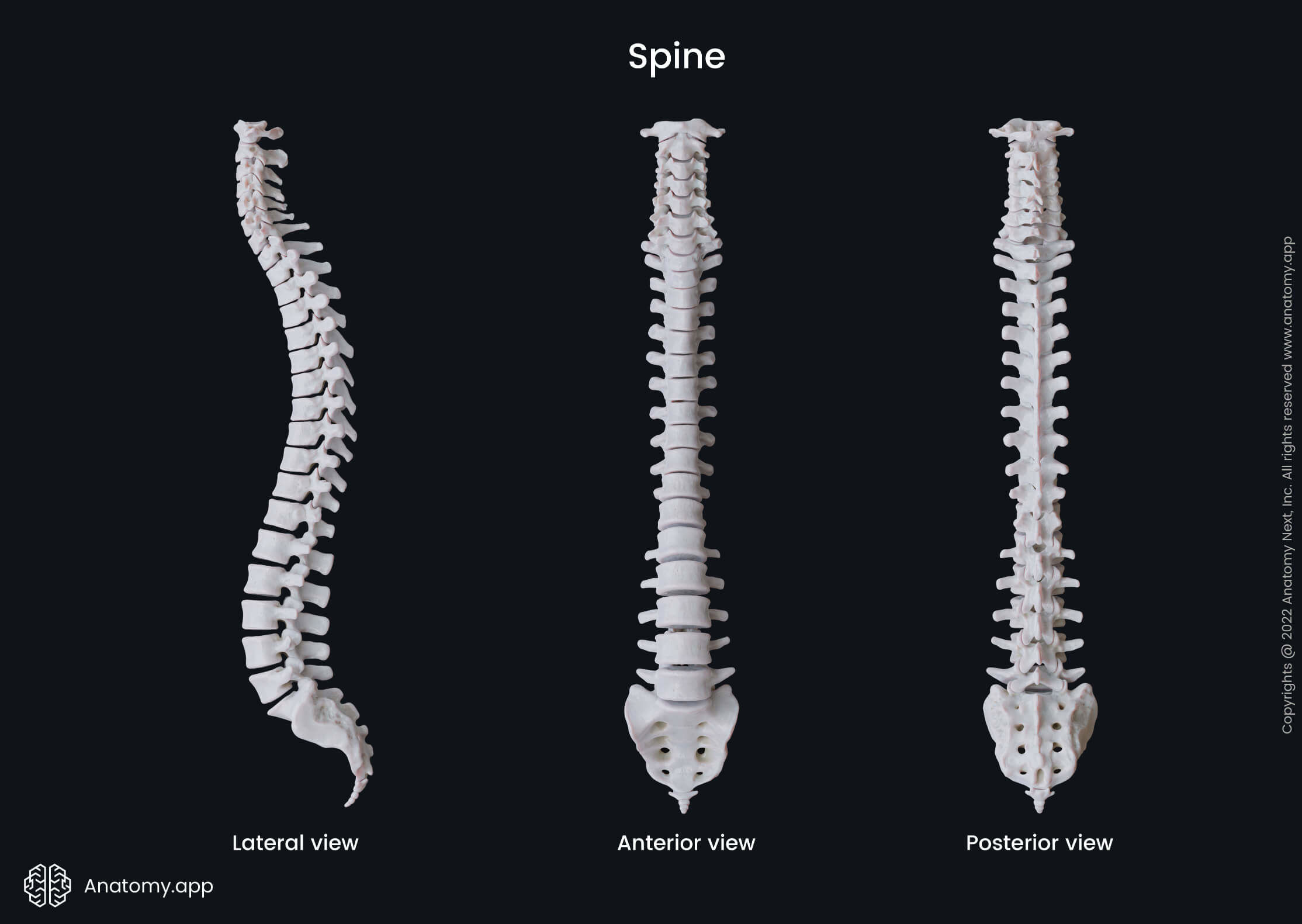
The vertebral column can be divided into the following parts:
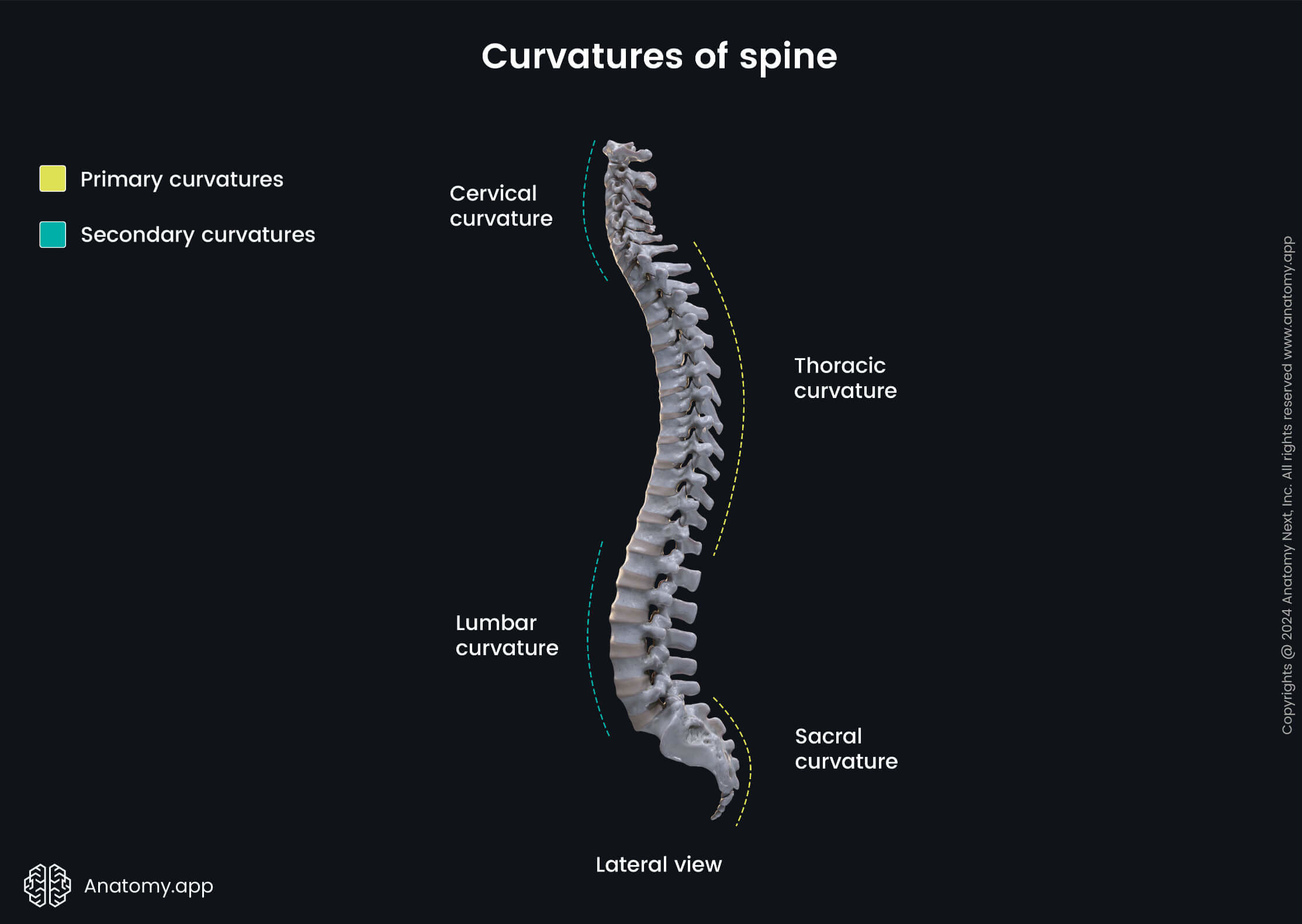 Curvatures of spine" width="1920" />
Curvatures of spine" width="1920" />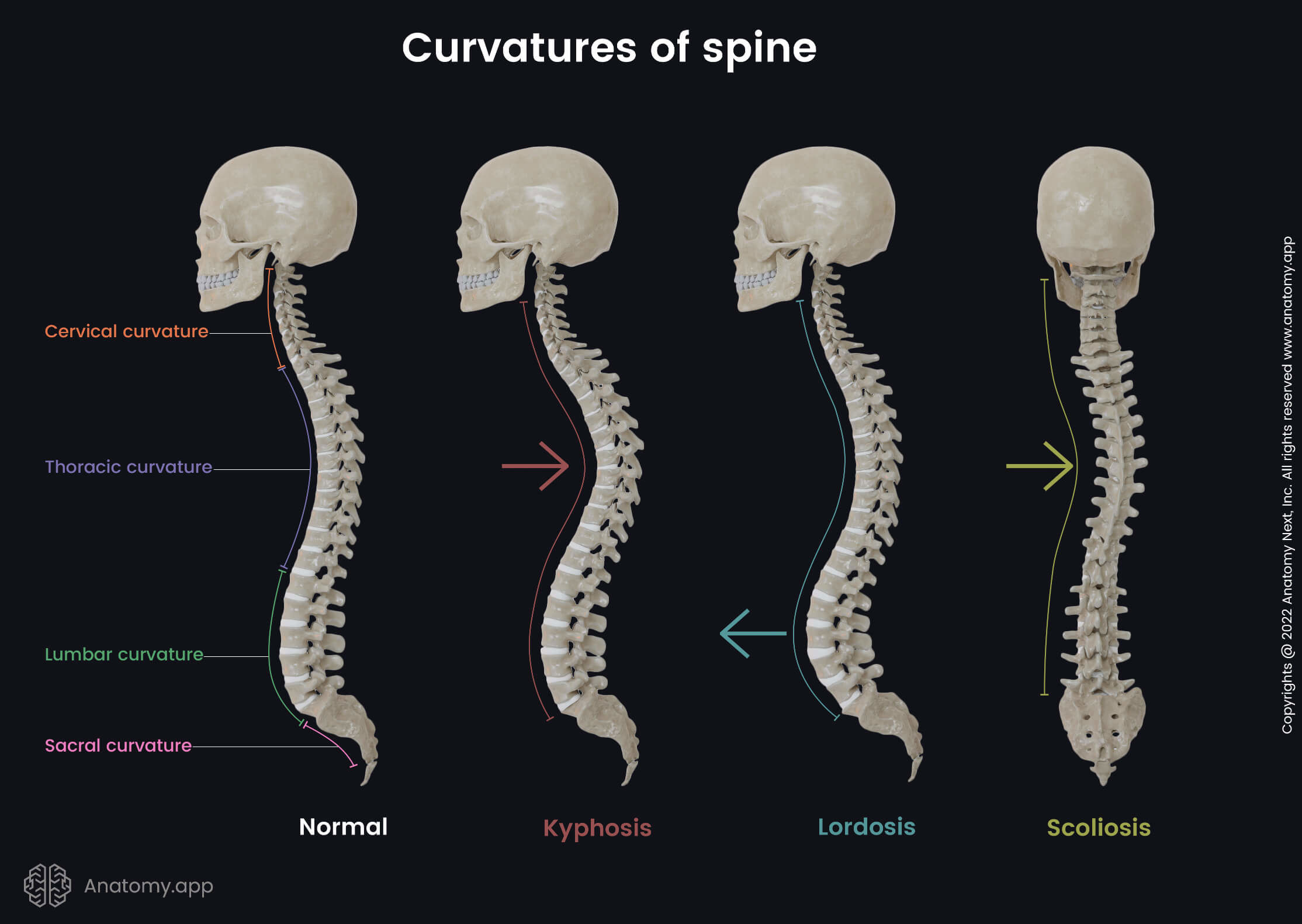 Curvatures of spine, Curves of spine, Normal spine, Healthy spine, Cervical curvature, Thoracic curvature, Lumbar curvature, Sacral curvature, Vertebrae, Skeleton of trunk, Human skeleton, Pathological curvatures, Pathological spine, Kyphosis, Lordosis, Scoliosis" width="1920" />
Curvatures of spine, Curves of spine, Normal spine, Healthy spine, Cervical curvature, Thoracic curvature, Lumbar curvature, Sacral curvature, Vertebrae, Skeleton of trunk, Human skeleton, Pathological curvatures, Pathological spine, Kyphosis, Lordosis, Scoliosis" width="1920" />